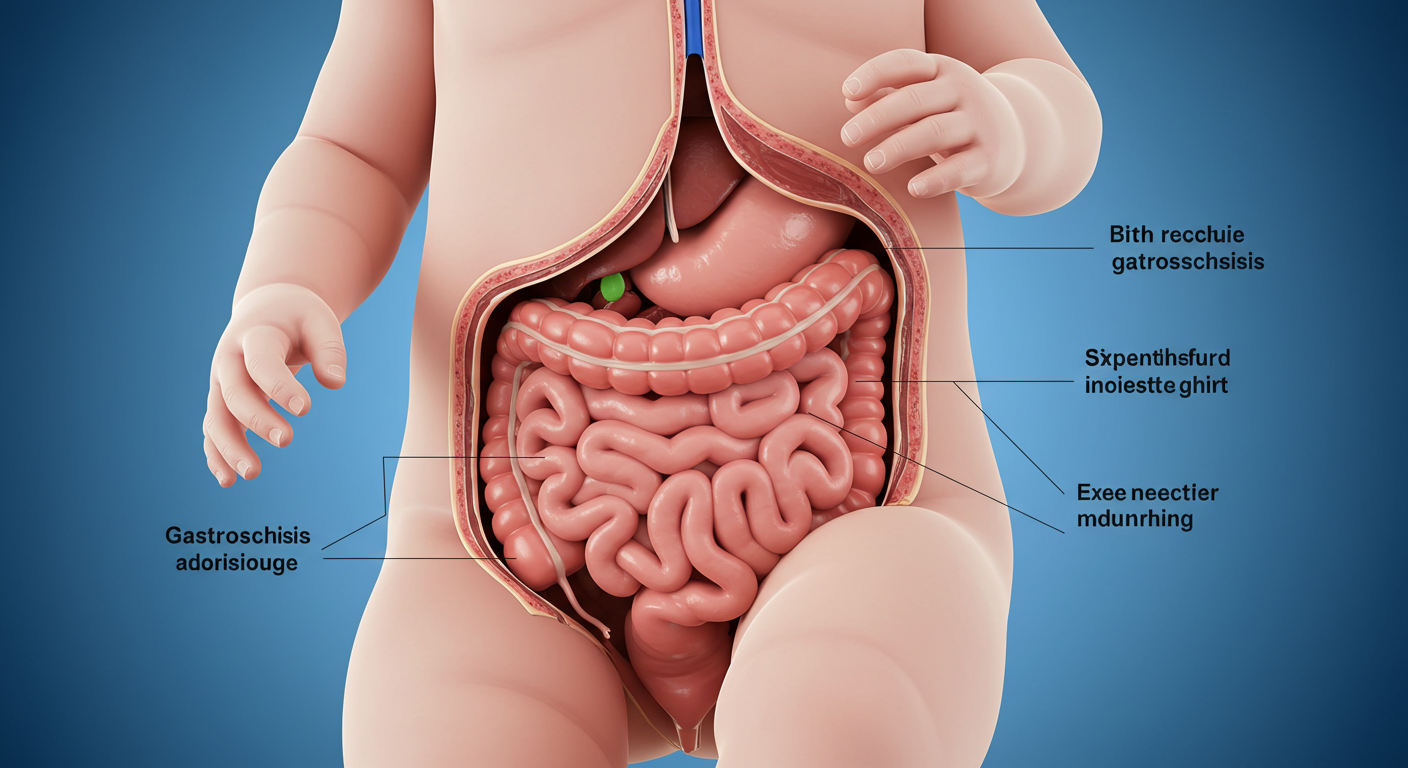
Gastroshiza is a complex condition that affects newborns, characterized by an abdominal defect where the intestines protrude outside the body. While it may sound alarming, understanding this condition can empower parents and caregivers to navigate its challenges more effectively. With early diagnosis and appropriate treatment, many babies with gastroshiza go on to lead healthy lives. This guide will explore essential information about gastroshiza—its signs and symptoms, causes, pathophysiology, treatment options, and how families can manage daily life in light of this diagnosis. Whether you’re a parent seeking answers or simply curious about gastrointestinal conditions in infants, you’ll find valuable insights within these pages. Let’s dive into the world of gastroshiza together!
Signs and Symptoms
Gastroshiza typically presents at birth, making it crucial for parents to recognize the signs early. The most noticeable symptom is the presence of the intestines protruding outside the abdominal wall. This can appear as a mass or bundle of tissue on one side of the baby’s body.
Newborns with gastroshiza may also exhibit other symptoms such as difficulty feeding. Due to their condition, they might struggle with proper latch-on during breastfeeding or refuse formula altogether.
In some cases, these infants could experience bowel obstruction or issues related to digestion. Signs like vomiting and lethargy may arise if there are complications associated with gastroshiza.
It’s essential for parents and caregivers to monitor any unusual behaviors in newborns closely. If you notice these symptoms alongside visible abnormalities in your baby’s abdomen, seeking immediate medical attention is vital for ensuring appropriate care and intervention.
You Might Also Like: Fonendi
Causes Of Gastroshiza Disease
The exact causes of gastroshiza remain largely unknown. Researchers believe it may stem from a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Certain maternal behaviors during pregnancy, such as smoking or drug use, might increase the risk.
Some studies suggest that a lack of folic acid in the mother’s diet could contribute to this condition. Folic acid plays a crucial role in fetal development, particularly in forming the neural tube and abdominal wall. When levels are insufficient, defects can occur.
Genetic mutations may also be involved. Families with previous cases of gastroshiza have shown higher incidences within their lineage, indicating potential hereditary links. However, no single gene has been pinpointed as responsible yet.
Environmental influences like exposure to toxins or medications during early pregnancy may further complicate matters. These elements can disrupt normal embryonic development and increase vulnerability to conditions like gastroshiza. Ongoing research aims to clarify these connections for better prevention strategies in the future.
Pathophysiology
Gastroshiza is a congenital defect where the abdominal wall does not close properly. This results in the intestines protruding outside the body, typically to the right of the umbilical cord. The condition arises during early fetal development, often before many women even know they are pregnant.
The pathophysiology involves disruption in mesodermal tissue formation. This essential layer contributes to forming various structures, including muscles and connective tissues that secure organs within the abdomen. If this process is abnormal, it can lead to openings that allow for herniation of intestinal contents.
Tissue exposure can also result in complications like inflammation or infection. The exposed bowel may suffer from damage due to environmental factors after birth unless surgical intervention occurs promptly.
Furthermore, associated anomalies may be present with gastroshiza; these can complicate treatment and recovery outcomes. Understanding these underlying mechanisms helps medical professionals devise effective management strategies for affected infants.
Diagnosing Gastroshiza
Diagnosing gastroshiza typically begins with prenatal imaging. An ultrasound can reveal the condition early in pregnancy, often around the 12th week. This critical step allows parents to prepare and seek specialized care.
After birth, doctors will conduct a physical examination of the newborn. They look for external signs such as intestines protruding through an opening beside the belly button. The size and appearance of this defect vary among individuals.
Further diagnostic tools may be employed if complications arise or additional conditions are suspected. Imaging studies like X-rays or CT scans help assess how much intestine is involved and whether there’s any associated bowel damage.
Timely diagnosis is crucial for planning treatment strategies effectively. It ensures that both medical teams and families understand what steps lie ahead in managing gastroshiza efficiently.
Treatment Of Gastroshiza Disease
The treatment for gastroshiza typically begins with immediate surgical intervention. This occurs soon after birth, as the condition involves the infant’s intestines protruding outside the body through a defect in the abdominal wall. Surgeons work to carefully return these organs to their rightful place and repair the opening.
In some cases, if there is significant swelling of the intestines or other complications, an initial step may involve placing a protective covering over them until surgery can occur safely. This approach helps to minimize risks associated with exposure while allowing time for stabilization.
Post-operative care is crucial for recovery. Monitoring will include ensuring proper bowel function and managing any potential infections. Infants often require nutritional support via IV fluids or feeding tubes until they can tolerate regular feedings.
As healing progresses, follow-up visits become essential to track growth and development. Parents should stay informed about their child’s needs as they navigate this journey toward health and well-being.
Prognosis
The prognosis for individuals with gastroshiza varies significantly based on several factors. Generally, when diagnosed and treated promptly, the outcome can be positive. Many infants born with this condition go on to live healthy lives after receiving appropriate medical care.
Timing is crucial in addressing gastroshiza. Early intervention often leads to better results. The administration of surgery shortly after birth tends to minimize complications associated with the protruding intestines.
However, some children may experience long-term issues related to their gastrointestinal function. This could include challenges like feeding difficulties or malabsorption syndromes, impacting their growth and development over time.
Regular follow-ups are essential for monitoring health and managing any potential complications that arise post-surgery. With proper medical support and an attentive caregiving approach, many families find strategies that help navigate daily life effectively while ensuring the child thrives despite their initial diagnosis.
Epidemiology
Gastroshiza is a rare congenital condition, with an incidence of approximately 1 in 5,000 to 10,000 births. It occurs more frequently in males than females. Understanding the demographic factors associated with this defect can provide insights into its potential causes.
Geographical variations have been observed, with higher rates reported in certain regions. For instance, it appears more prevalent among populations in North America compared to Europe or Asia. These disparities raise questions about environmental and genetic influences.
Additionally, maternal age plays a significant role; younger mothers tend to have higher risks for gastroshiza pregnancies. Nutritional factors during pregnancy might also contribute to these statistics and warrant further investigation.
Despite being classified as a rare disorder, awareness is crucial for early detection and treatment options. Continued research will help clarify the underlying epidemiological trends related to gastroshiza while promoting effective preventive measures for expectant mothers.
Prevention tips and healthy habits
Staying informed is key to reducing the risk of gastroshiza. Expectant mothers should prioritize regular prenatal care. This ensures early detection and monitoring of any potential issues that could affect fetal development.
Nutrition plays a crucial role in preventive measures. A balanced diet rich in essential vitamins and minerals supports healthy pregnancy outcomes. Foods high in folic acid are especially important, as they help reduce neural tube defects linked to various congenital conditions.
Additionally, avoiding harmful substances can significantly lower risks. Pregnant women should refrain from smoking, alcohol consumption, and exposure to toxic chemicals whenever possible. These habits not only benefit maternal health but also promote proper fetal growth.
Staying physically active within safe limits contributes positively to overall well-being during pregnancy. Gentle exercises like walking or prenatal yoga can enhance physical fitness while reducing stress levels for both mother and child.
You Might Also Like: Diag Image
Managing daily life with Gastroshiza
Managing daily life with Gastroshiza can be a unique journey. It often requires adjustments and support from family, friends, and healthcare providers. Those diagnosed with this condition may face challenges related to feeding, nutrition, and general health.
Establishing a strong support network is crucial. Connecting with others who share similar experiences can provide comfort and valuable insights on coping strategies. Many find that joining online forums or local support groups helps them feel understood.
Nutrition plays a significant role in managing gastroshiza post-surgery. Working closely with dietitians ensures that dietary choices are both safe and nourishing. Regular follow-up appointments with healthcare professionals help monitor progress and address any concerns promptly.
Emotional well-being shouldn’t be overlooked either. Consider speaking to mental health professionals if feelings of anxiety or stress arise during the recovery process. They can offer tools for coping effectively.
Daily routines may need modifications too; simple tasks might require extra planning initially but become easier over time as one adapts. Emphasizing small victories fosters positivity amid challenges.
Engaging in light physical activity when approved by doctors promotes overall health and aids recovery while providing a sense of normalcy in everyday life.
Finding joy in little things makes each day brighter despite the circumstances faced due to gastroshiza.